Oxygen therapy, also known as supplemental oxygen, is the use of oxygen as a medical treatment. These treatments can be intended for diseases, characterized by a low percentage of oxygen in the blood, carbon monoxide poisoning, headaches, and to maintain a sufficient amount of oxygen such as; Obstructive lung diseases such as COPD, retractive diseases such as pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension and various heart diseases, headaches, chronic exhaustion, muscle molasses, fibromyalgia and more.
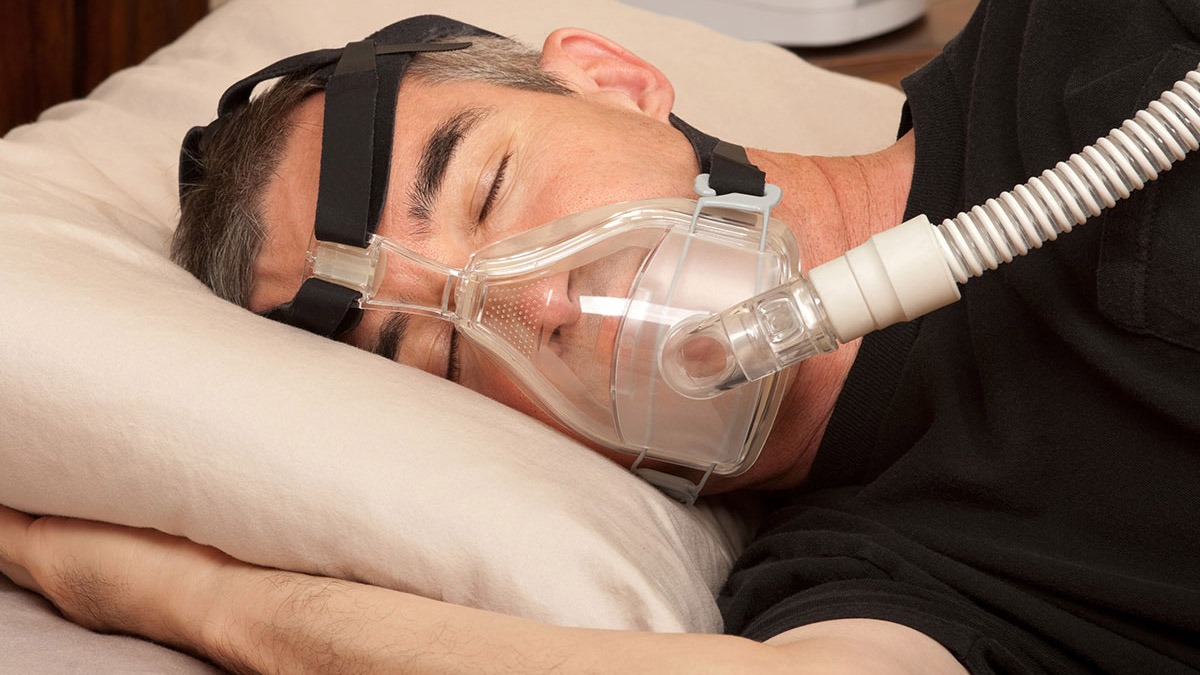
Long-term oxygen therapy can be effective for people with low oxygen percentage, such as people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or cystic fibrosis. Oxygen can be administered in several ways, including a nasal tube, a face mask, and inside a hyperbaric chamber (pressure chamber).
It can also be used by other people whose injury or illness has led to low oxygen levels.
The exceptions to these proposals are those with carbon monoxide poisoning, cluster headaches, attacks of sickle cell disease, and cases of air chest.
For personal use, oxygen in high concentrations is used as a home treatment to prevent bouts of cluster headaches.